#KidneyWk 2018: FIT Bowl Finals – JEOPARDY!
As a kid who grew up participating in Scholar Bowl, and who religiously turned on the TV at 3:30 pm to watch Alex Trebek, nothing is better than medical jeopardy. This year’s #KidneyWk 2018 finals competition pitted the Arkansas Aquaporins @UAMSNeph against the Renal Rockstars @BWHKidney/@MGHKidneys. Note: Semifinals coverage here.
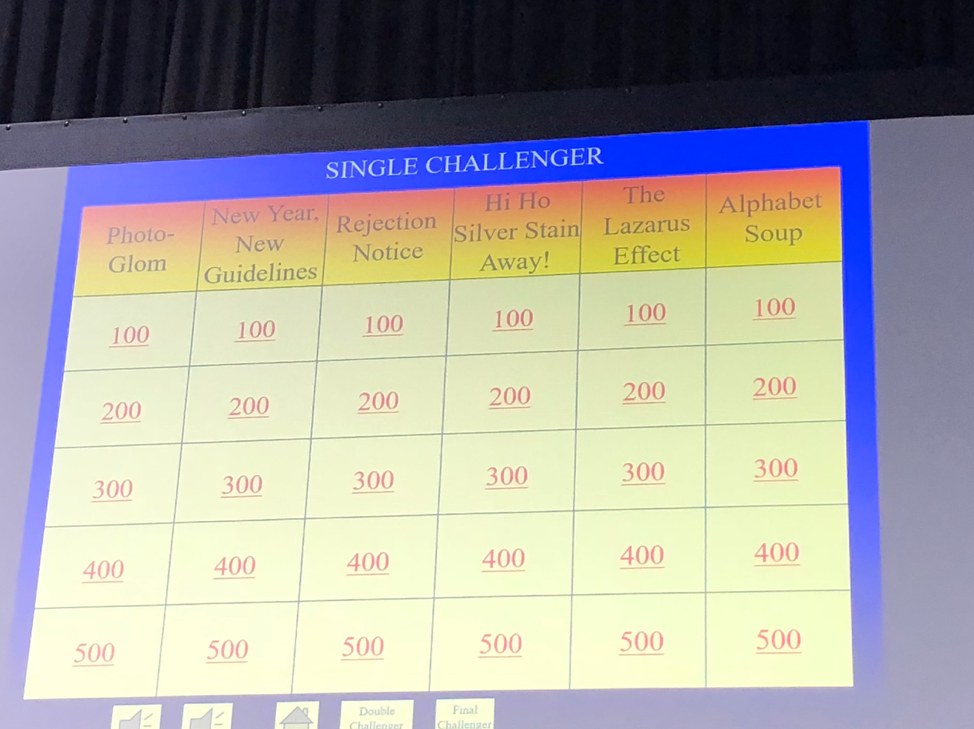
The rules were the same as Jeopardy, minus the daily doubles. There was a single, double, and final jeopardy round, and teams were penalized for incorrect responses. The categories for the single and double Jeopardy round were:

Congrats to @MGHKidneys/@BWHKidney Renal Rockstars for winning this year’s FIT Bowl challenge!
Test your own knowledge with a sampling of questions from these diverse categories:
- This hybrid between IHD and CVVHDF provides for longer dialysis treatments while giving the ICU patient some downtime for procedures.
- This antihypertensive medication can cause drug-induced lupus or ANCA vasculitis.
- This immunosuppressive agent targets the cell surface antigen CD-52.
- This phenomenon refers to the lack of usual nocturnal all in blood pressure.
- Disorder characterized by a total-to-ionized calcium ratio greater than 2.5 in a patient on CRRT.
- This location of dialysate infusion in CVVH decreases circuit clotting but also decreases efficiency.
- This term refers to hypertension induced by compression of the renal parenchyma.
- These three things currently comprise the standard of care treatment regimen for early acute antibody mediated rejection.
- Immediate therapy for a woman receiving magnesium for preeclampsia who develops flaccid paralysis.
- Hypernatremia in peritoneal dialysis can occur during rapid, frequent exchanges due to this phenomenon.
- This buffer is effective in both respiratory and metabolic acidosis.
- Sipple syndrome features this form of secondary hypertension.
- This routine serologic evaluation is performed to characterize if a donor might be a Public Health Service Increased Risk Donor (PHS IRD).
- The PATHWAYS 2 trial showed efficacy of this antihypertensive medication for resistant hypertension.
- These are the only biomarkers approved by the FDA for risk-assessment of potential for AKI.
- In chronic hemodialysis patients, ultrafiltration rates above this level have been associated with all cause and cardiovascular mortality.
- This serum electrolyte disorder is seen in individuals with a mutation in claudin-16.
- Proton pump inhibitors are associated with this form of nephrotoxicity.
- Ingestion of this alcohol can cause ketonemia without acidosis.
- Because of renal retention of its metabolite, M6G, this analgesis should not be used in repeated doses in patients with renal failure.
- The X-linked inherited disorder that can manifest as neuropathic pain, telangiectasias, angiokeratomas, proteinuric renal disease, LVH, and strokes is caused by a deficiency in this.
- This is the most common renal complication of sickle cell disease and is most often heralded by overt nocturia.
- In addition to acute tubular necrosis, this antibiotic can also cause a picture that mimics Bartter syndrome.
- Hungry bone syndrome and refeeding syndrome can both cause this electrolyte disorder.
- This anticonvulsant can cause metabolic acidosis without Fanconi syndrome through inhibition of carbonic anhydrase.
- A 16-year-old hypertensive female with low renin, low aldosterone, metabolic acidosis, and hyperkalemia most likely has this disorder.
- The use of D-penicillamine in cystine stone therapy is often limited by this renal disorder.
- This ingestion causes what looks like an RTA but is really due to increased urinary excretion of Hippurate.
- The inherited renal disorder associated with nephromegaly, systemic hypertension, portal hypertension, and pruritis.
- Also known as “Spice” or “K2,” this type of recreational drug has been associated with AKI due to ATN or AIN.
- A 30-year-old man with nephrocalcinosis, kidney stones, hypercalciuria, low molecular weight proteinuria, and a serum creatinine of 2 mg/dL most likely has this disorder.
- This mutation can cause CAKUT with progressive CKD, diabetes mellitus due to pancreatic agenesis, hyperuricemia and renal magnesium wasting.
- Although unusual, the acute presentation of isolated postpartum diabetes insipidus may be due to placental production of this.
Scroll down for answers!
- What is SLEDD? (slow low efficiency daily dialysis)
- What is hydralazine?
- What is alemtuzumab (Campath)?
- What is non-dipping?
- What is citrate toxicity?
- What is pre-filter, or predilution?
- What is Page kidney?
- What is IV methylprednisolone, plasmapheresis, and IVIG?
- What is IV calcium (either gluconate or chloride)?
- What is sodium sieving?
- What is tromethamine (or THAM)?
- What is pheochromocytoma?
- What is nucleic acid testing (NAT) for HIV, Hep B, Hep C?
- What is spironolactone?
- What are TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7 (nephrocheck)
- What is 13 cc/kg/hr?
- What is hypomagnesemia?
- What is interstitial nephritis?
- What is isopropyl alcohol?
- What is morphine?
- What is alpha galactosidase?
- What is a urinary concentrating defect?
- What is gentamicin?
- What is hypophosphatemia?
- What is topiramate?
- What is Gordon’s syndrome (Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2)?
- What is membranous nephropathy?
- What is toluene?
- What is autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)?
- What are synthetic cannabinoids?
- What is Dent’s disease?
- What is HNF1B (hepatic nuclear factor 1-beta)
- What is vasopresinase?
– Post prepared by Timothy Yau, AJKD Social Media Editor. Follow him @Maximal_Change.


Leave a Reply